Search Engine Optimization
#4 Indexing of your webpages
How search engines interpret and store your webpages
Index is where your webpages are stored
Being discoverable and crawled by a search engine does not guarantee that your site will be indexed. When a crawler finds a page, the search engine analyzes its content, renders it as a browser would, and stores all the information in its index. The index is where your discovered pages are stored.
View how a Googlebot crawler sees a webpage
Google crawls and stores web pages in its cache at varying intervals. To see the cached version of a page, click on the drop-down arrow adjacent to its URL on the SERP and select “Cached.”
Another way to assess if your important content is being crawled and cached efficiently is to view your site’s text-only version.
How Google builds its search index
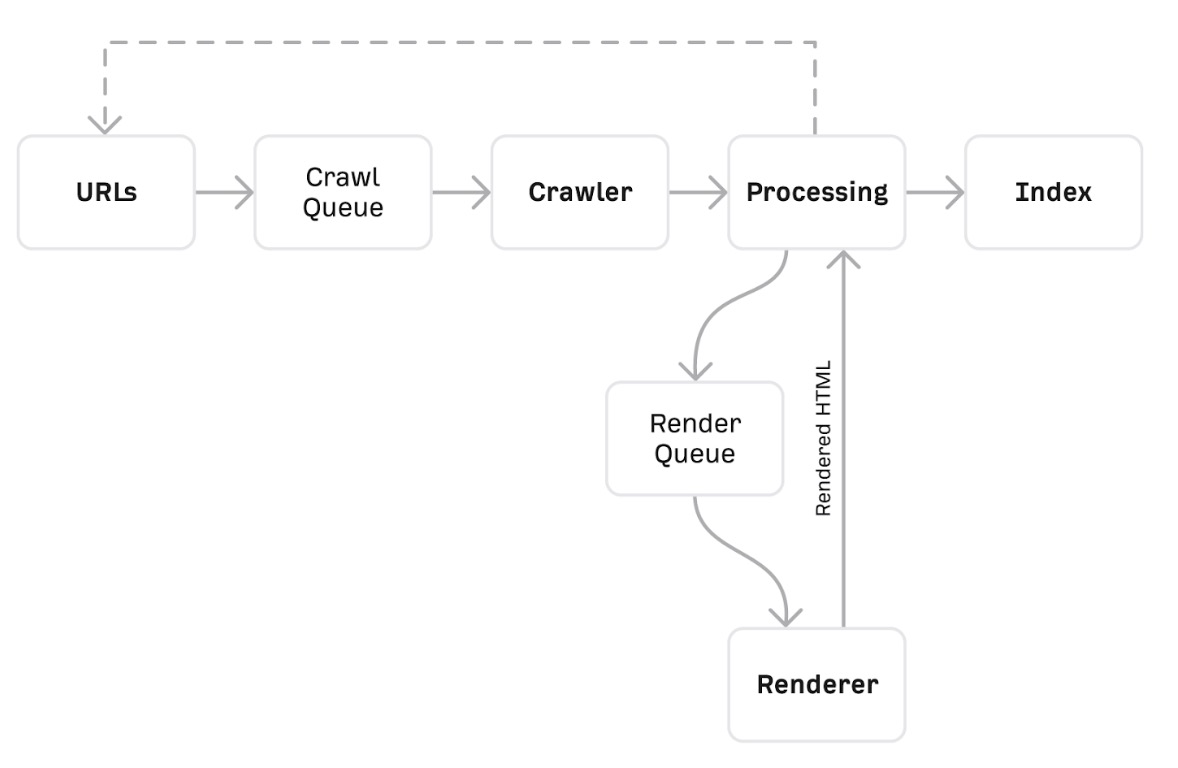
The indexing process begins with a known list of URLs. Google discovers these in several ways.
Crawling is where a computer bot called a spider visits and downloads known URLs. Google’s crawler is called Googlebot.
Processing is where Google works to understand and extract key information from crawled pages. In order to do this, it has to render the page, which is where it runs the page’s code to understand how it looks like for users.
Indexing is where processed information from crawled pages gets added to the search index.
The search index is what you search when you use a search engine. That is the reason why it is important to get your website indexed in Google. Your website cannot be found unless it is indexed.
Tell search engines how to index your website
By comprehending the various methods that can impact crawling and indexing, you can evade typical traps that may hinder the discovery of your crucial web pages.
Robots meta directive
The robots meta tag can be used within the HTML of your webpage. It can exclude all or specific search engines. The following are the most common meta directives and what situations you might apply them in.
Search engine ranking
Index / no index
This option guides search engines on whether to crawl and include the page in their index for future retrieval. If you choose to utilize the “no index” option, you are indicating to search engine crawlers that you wish to exclude the page from appearing in search results.
Follow / No follow
This tells search engines whether links on the page should be followed or not followed.
No archive
Optimize your title tags and meta descriptions to improve the click through rate of your webpages.
