Search Engine Optimization
#7 On-page SEO
On-page SEO
Work on items you are in control of
The top search engine results are where people anticipate finding what they seek online. If your website is ranked at the top of the search engine results page, enticing new customers to your business becomes more accessible. Developing a robust search engine optimization strategy is among the most beneficial investments you can make for your business.
On-page SEO is concerned with creating a website appealing to users and search engines. It pertains to SEO methods and elements that concentrate on enhancing aspects of your website that are within your purview, such as generating content.
Creating your content
“Ten times better”
Google determines which pages to rank highly based on whether they are the best answers to the searcher’s questions. To rank well, your page must provide value to searchers and be superior to any other page that Google currently serves as the answer to a specific query.
To create compelling content, follow these steps:
- Search for the keywords you want your page to rank for.
- Identify which pages are currently ranking highly for those keywords.
- Determine what qualities those pages possess.
- Create content that surpasses those pages in quality.
However, one strategy works particularly well: creating content that is ten times better than your competitors, also known as the “ten times better” strategy. If you make a page on a keyword ten times better than the pages currently shown in search results, Google will reward you, and people will naturally link to it. Creating ten-times content is challenging but will pay off in organic traffic. Consider the following six points when creating ten-times content.

Better quality
- Cover the topic more thoroughly than your competitors
- Provide more up-to-date information and data
- Provide more expertise and trustworthiness
- Be original, use unique data and provide new angles
- Link to other relevant resources of high quality
Better design
- Use a unique layout for your most important pieces of content
- Add visually stunning media (illustrations, infographics, charts, gifs, screenshots, videos)
- Use your own illustrations and avoid stock photos
Better user experience UX
- Make sure the text is readable and free of grammar errors
- Write short and use easy-to-digest paragraphs
- Use navigational elements such as table of contents for longer pages
- Use quotes, info boxes, bulleted lists, bolded sentences
- Optimize the technical aspects
Content length
Although it’s commonly believed that Google favors longer content, it’s not the actual length of the content that determines its rank. Instead, longer posts typically provide a more comprehensive and in-depth discussion of the topic, which is what search engines prioritize.
Some individuals assume that content length is a key factor in rankings. A study conducted by Backlinko even revealed that posts with roughly 1500 words ranked higher on Google.
So, how should you approach content length?
- Consider the average word count of the pages that rank for your targeted keyword to understand how long your content should be.
- Ensure that your content comprehensively covers the topic and provides readers with all the necessary information they might be looking for.
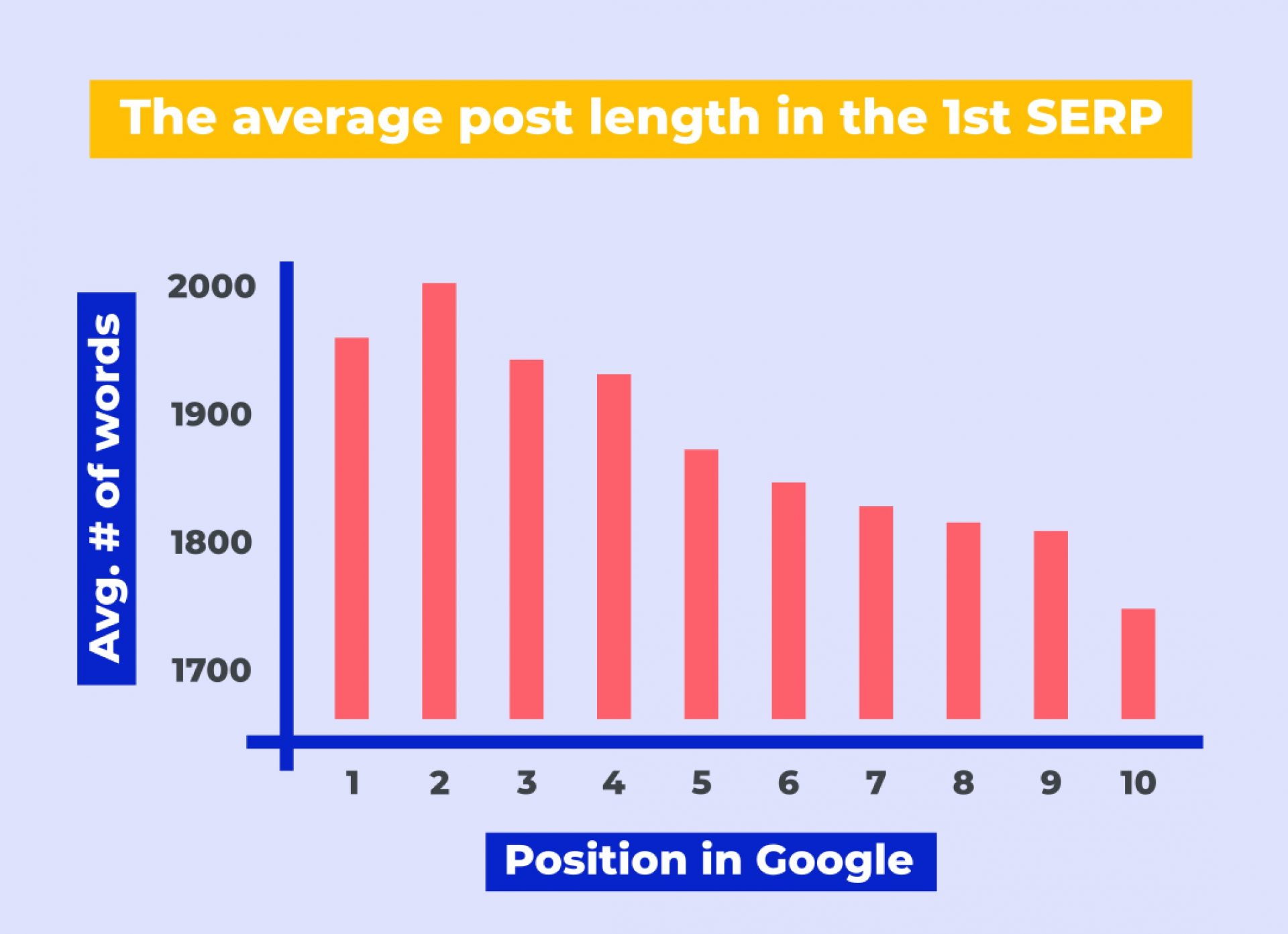
- Always keep in mind that a high number of words alone will not improve your rankings. Focus on the quality of content, not just quantity.
Content updates
Content decay is a real thing. No matter how successful a piece of content is, there’s a big chance the traffic will gradually decrease unless you keep it fresh and updated. Andrew Tate noticed that many successful blog posts share the same traffic curve and described this phenomenon as the 5 phases of the content lifecycle:
- Spike phase, when the post is first published.
- Trough phase, where it looks like growth is stagnant.
- Growth phase, as pageviews increase over a few months.
- Plateau phase, as growth levels out.
- Decay phase, as traffic to the post starts to drop off.
So, how to make sure your post is remembered over time? The answer is regular updates. Regular content updates are an essential SEO technique. One of the reasons content updates may positively impact your rankings is that Google notices the frequency of updates and tends to favor frequently updated pages for some queries.
Updating vs. republishing
Smaller changes of your pages don’t require any special steps. However with a major remake it is probably worth republishing the post. By doing so it shows at the top of your blog feed and the readers know the post went through a big update.
Here are some cases when you may consider republishing your post:
- The update affects more than 50% of the content.
- You have added a significant amount of new content.
- You have merged two or more posts into one.
Republishing is also a great opportunity to promote your post again on social media and newsletter or starting a new link building campaign.
Local business
If you’re a business that makes in-person contact with your customers, be sure to include your business name, address, and phone number (NAP) prominently, accurately and consistently throughout your site’s content. This information is often displayed in the footer or header of a local business website, as well as on any “contact us” pages. You can make use of this local business schema to ensure you have all contact details covered.
Local vs. national vs. international
Just remember that not all businesses operate at the local level and perform what is called “local SEO“. Some businesses want to attract customers on a national level and others want to attract customers from multiple countries (international SEO). How you choose to optimize your site depends largely on your audience, so make sure you have them in mind when crafting your website content.
Beyond content: Other optimizations your pages need
Header tags
The HTML element used to indicate web page headings are header tags. The H1 tag, the primary header tag, is usually used for the page title, while H2 to H6 tags are reserved for subheadings. However, including all of these tags are not mandatory. The order of header tags follows a hierarchy, with H1 being the most important and H6 being the least.
It is recommended to have a unique H1 tag for each page that summarizes the main topic. In most cases, the H1 tag is automatically generated from the page title. The H1 tag should include the primary keyword or phrase related to that page’s content.
Internal links
Internal linking structure is often overlooked in SEO, but it plays a crucial role in a website’s crawlability. While external backlinks are important, having a well-designed internal linking structure is equally crucial.
By linking to other pages on your website, you make it easier for search engine crawlers to find and index all your pages and pass ranking power to other pages and improve visitors’ navigation experience.
There are three reasons why internal links are important:
- They improve the crawlability of your website. By linking pages within your site, search engine crawlers can easily find and index all your pages.
- They enhance user experience and engagement. By providing straightforward navigation and relevant contextual links, visitors can easily find what they are looking for and spend more time engaging with your content.
- They can boost your rankings. Internal links pass link equity, and if a page has a lot of relevant internal links with descriptive anchor texts, Google will consider it essential within your page structure and give it more prominence.
The golden rule of internal linking is to ensure that any page is at most three clicks away from your homepage.

Title tags
The title tag of a webpage is an HTML element that specifies the title of that particular page and is located within the head tag of each page.
To optimize your website for search engines and users, it is crucial to have a unique and descriptive title tag for each page. The text you provide in your title tag field will be displayed in search results, but Google may sometimes modify how it appears.
The title tag plays a significant role in shaping a visitor’s first impression of your website, making it a powerful tool for attracting searchers to your page instead of other results on the search engine results page. A compelling title tag, coupled with high search result rankings, can significantly increase traffic to your website.
This highlights that SEO is about pleasing search engines as well as and providing a positive user experience.
URL structure; naming and organising your pages
URL is an acronym for Uniform Resource Locator, essentially the web address of a particular piece of content. Along with title tags and meta descriptions, URLs are shown on search engine results pages (SERPs), meaning their naming and formatting can influence click-through rates. URLs are crucial for helping searchers make decisions about which web pages to visit and are also used by search engines to assess and rank web pages.
Clear page naming
To have your website pages appear in search results, each page must have a unique URL. Having a clear URL structure and naming convention is also beneficial for users trying to understand the content of a specific URL. URLs that reinforce and clarify the information contained on a page are more likely to be clicked by searchers, while confusing URLs are less likely to be clicked.
While URLs are a minor ranking factor, it’s not enough to rely on the words in your domain or page names to rank higher (as seen in the Google EMD update). Therefore, when naming your pages or choosing a domain name, prioritize your target audience’s needs and preferences.
URL length
Although a completely flat URL structure is not required, studies on click-through rates show that searchers generally prefer shorter URLs when presented with a choice. Like title tags and meta descriptions, excessively lengthy URLs will be truncated with an ellipsis. However, it’s important to remember that descriptive URLs are just as essential, and it is not advisable to compromise descriptiveness to shorten the URL.
Clear page naming
Ensure that your page’s targeted term or phrase is included in the URL, but avoid overdoing it by adding multiple keywords solely for SEO purposes. It’s also crucial to avoid repeating keywords in different subfolders. For instance, a keyword may have been naturally included in a page name. However, if it’s in other folders optimized with the same keyword, the URL could look like it’s stuffed with keywords.
Overusing keywords in URLs can come across as manipulative and spammy. If you need more clarification on whether your keyword usage is too aggressive, read your URL like a searcher and ask yourself, “Does this look natural? Would I click on this?”
